Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 2 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-02-14 Origin: Site
In the field of physics and engineering, torque, torque, torque and bending moment are important physical quantities that describe the rotation or bending effect of an object after the force. Although these terms are often mentioned in daily communication and academic research, they each have unique definitions, application scenarios, and differences and connections. This paper aims to explore the essential differences and internal connections of these four concepts in order to provide a clearer cognitive framework for learners and practitioners in related fields.
1. Definitions and basic concepts
1.(Moment of Force)
The moment is the physical quantity that describes the rotational effect of a force on a point or axis. Its size is equal to the product of the force and the force arm (i. e., the vertical distance between the action of the force to the point of rotation), with the direction perpendicular to the plane of the force arm, determined by the right-hand helical rule. Torque is a fundamental and key concept in physics. It is not only the cause of angular acceleration, but also an important tool for analyzing lever balance, rotational motion and stability of mechanical system.
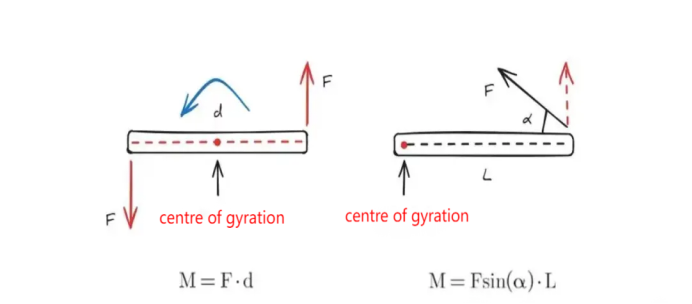
2. Torque
Torque is the specific application of torque in rotating machinery, which specifically refers to the torque that makes the object produce rotational motion around a certain axis. In physics and engineering, the torque is a vector equal to the product of the force and the force arm, but the direction is along the axis of rotation. Torque is one of the key indicators to measure the rotational mechanical performance, widely used in the design and performance evaluation of rotary equipment such as motor, gear and drive shaft.
It should be noted that in some literature or contexts, torque and torque are regarded as synonyms, which are used to describe the torque action on the rotating object. However, in rigorous academic research, it is common to distinguish between the two according to the specific situation. Here, we use torque to describe the torque action of a rotating object, while torque is more used interchangeably with torque in a specific context (e. g., engineering practice).
3. Torque(Synonymous with the torque in a specific context)
Torque is a term that is used interchangeably with the torque in a particular context, especially in engineering practice. It represents the rotation effect of a force on the axis of rotation, the size is equal to the product of the force and the force arm, the direction along the axis of rotation. In the automotive, mechanical and other engineering fields, torque is an important indicator to measure the engine performance, transmission system efficiency and vehicle acceleration capacity. In addition, the torque is also closely related to the material strength, structural stability and service life of the object.
4. Bending Moment
The bending moment is the physical quantity that describes the bending deformation effect of an object when subjected by an external force perpendicular to the axis. When the object is subjected to an external force, and the action line of this external force does not pass through the center of mass of the object, the bending moment is generated inside the object. The size of the bending moment is determined by the external force and the force arm, the direction is perpendicular to the force plane, and the point of action is usually located on the axis or section of the object. The bending moment is one of the important factors that must be considered in structural engineering, which is directly related to the safety, stability and service life of the building.
Table 1 Shear force diagram and bending moment diagram of basic beams under simple loads
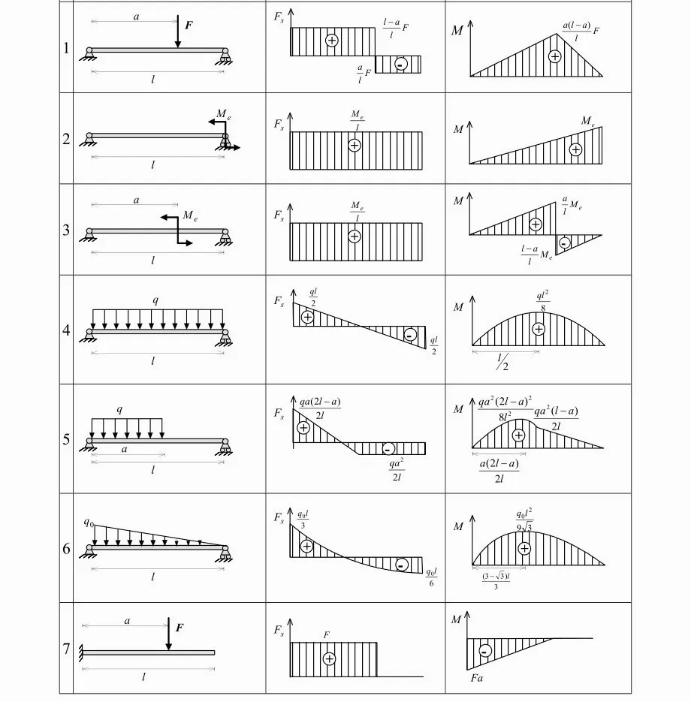
2.1. The force moment is a broad concept, covering the result of the force multiplied by the force arm, which describes the nature of the rotation effect of the force on an object. It is applicable not only applicable to rotating objects, but also on stationary objects. Torque specifically refers to the torque action of the rotating object, paying attention to the torsional deformation effect in the process of rotation and the characteristics of the rotating movement. Torque is used interchangeably with torque in a specific context (e. g., engineering practice), but is often more often used to describe the effect of objects in the direction along the axis, such as the torque generated by the engine. The bending moment focuses on describing the bending deformation effect of the object when it is subjected to an external force perpendicular to the axis
The calculation method and the calculation formula of directional torque, torque and torque are all the product of force and force arm, but the direction is different. The direction of the torque and torque is perpendicular to the plane where the force and force arm are located, while the direction of torque is along the axis of rotation. The direction of the bending moment is perpendicular to the force plane. In the process of calculation, it should also pay attention to the influence of the action point and direction of the external force and the geometry and size of the object on the moment, torque and bending moment.
2. Physical meaning and application scene torque is the cause of the angular acceleration of the object, which can change the rotating motion state of the object. It has important applications in lever balance, rotational motion and mechanical system stability analysis. Torque is one of the key indicators to measure the rotational mechanical performance, widely used in the design and performance evaluation of rotary equipment such as motor, gear and drive shaft. Torque is an important index to measure engine performance, transmission system efficiency and vehicle acceleration ability, and it is widely used in automotive and mechanical engineering fields. The bending moment is one of the important factors that must be considered in structural engineering, It is directly related to the safety, stability and service life of the building. In the design and analysis of bridge, building and other building structures, the calculation and analysis of bending moment is very important.
The basic calculation formula of torque, torque, torque and bending moment all involve the product of force and distance, which reflects the internal connection between them. Although their application scenarios, directionality and physical significance are different, the factors such as the action point of the external force, the direction and the geometry and size of the object should be considered in the calculation process. Whether it is the torque, torque, torque or bending moment, they are all the physical quantities that describe the effect of the force on an object. These effects may manifest as rotational motion of the object, torsional deformation or bending deformation, etc. Therefore, in the analysis and design of mechanical system, the role of these physical quantities and mutual interaction.
3. Interchangeably used in a specific context (e. g., engineering practice), torque and torque can be used interchangeably because they both describe the torque action of a rotating object. At the same time, in some situations (such as when analyzing the rotation effect of objects), the torque and torque can also be considered as similar concepts. However, in rigorous academic research, these terms are often distinguished according to the specific context to avoid confusion.
4. Conclusion Momque, torque, torque and bending moment seem similar on the surface, but