Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 3 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-02-08 Origin: Site
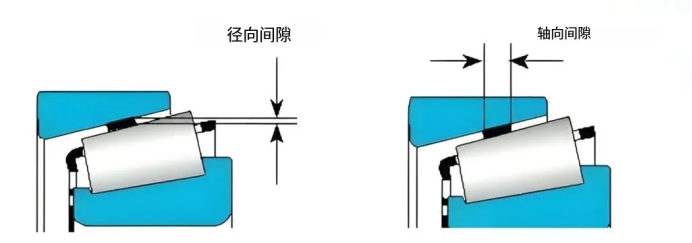
The radial swimming gap (Radial Clearance) rolling body is in the gap perpendicular to the bearing axis, affecting the bearing capacity, vibration and noise of the bearing.
The clearance of the axial gap (Axial Clearance) rolling body along the axis of the bearing mainly affects the axial positioning accuracy of the bearing.
According to the ISO 5753 and GB / T 4604 standards, the radial swimming gaps are usually divided into several grades, such as C2, C0 (standard), C3, C4, C5, etc., in which:
C2: minimum swimming gap, suitable for high precision, low vibration occasions.
C0: Standard gap, suitable for general applications.
C3~C5: Large gap is suitable for high temperature and high load conditions.
2. Influence of bearing gap on vibration and noise
2.1 Cause vibration and impact noise
When the radial swimming gap is too large, the bearing rolling body will have an impact during the operation process, resulting in the unstable contact between the inner and outer rings of the bearing, mainly manifested as:
The low-frequency vibration increases, and the operation is unstable.
The impact noise of rolling body and rolling road is intensified, resulting in the increase of equipment noise.The bearings may be unstable during operation, resulting in additional wear.
Experimental data show that in a motor bearing test, by increasing the standard gap C0 to C4, the measured vibration value is increased by about 30%, and the noise level increases by about 4~6dB.
3. Function of bearing tolerance control on life and stability
3.1 Relationship between bearing gap and service life
Reasonable swimming gap can optimize the rolling contact state and extend the bearing life.
Experiments show that C0 or C3 gaps can provide optimal vibration control and life balance under conventional conditions.
3.2 Tolerance control optimization strategy
To ensure the stability and life of the bearings in different application scenarios, the tolerance control should be optimized, including:
Accurately control the bearing, shaft, bearing seat coordination to avoid excessive surplus or too small clearance.
Considering the influence of working temperature on swimming gap, it is recommended to choose C3 and above to compensate for the size change caused by thermal expansion.
Optimize the lubrication mode to ensure the stability of the lubricating oil film within the swimming range, and reduce the noise and friction wear.
4. Example analysis of bearing gap selection
Case 1: High-speed motor bearings
Operating condition: motor speed 12,000 rpm, temperature 80℃, requiring low noise operation. Optimization scheme: select C3 gap bearing to ensure that the gap is kept in a reasonable range after temperature rise, and use low noise grease. Results: vibration level was reduced by 15%, noise reduced by 5dB, and bearing life increased by 30%.
Case 2: Heavy-load construction machinery bearings
Working condition: excavator rotary bearing, low speed and heavy load, large temperature change in working condition. Optimization scheme: use C4 gap to avoid bearing jamming due to load and thermal expansion and cold contraction, and use high viscosity grease. Results: Reduce the rolling body impact and improve the bearing life by 20%.