Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-01-27 Origin: Site
The equipment operates in a harsh environment with large temperature difference between day and night or under the condition of large temperature difference before and after the start, and the tightening performance of bolts and screw holes will be significantly affected due to thermal expansion and cold contraction. Especially for the application scenario of thin-walled screw hole, the difference of thermal expansion coefficient of material directly determines the change of fastening force. This paper will start with the influence of temperature difference on the tightening force of bolt and screw hole, analyze the mechanism of thermal expansion difference, and put forward the design and material selection to adapt to the temperature difference environment.
1. The influence mechanism of temperature difference on bolts and screw holes
In the temperature difference environment, the thermal expansion coefficient of each component of the equipment is different, and the bolts and screw holes will produce additional stress due to the inconsistency of expansion or shrinkage degree, which will affect the tightening force. The main mechanisms are described as follows:
1.1 Stress change caused by the difference in thermal expansion
Material difference in thermal expansion coefficient The difference in thermal expansion coefficient of different materials can lead to the relative displacement between bolts and screw holes, which causes the pretension force change or loosening.
When the temperature difference between day and night is large, the heating or cooling rate of the equipment is not consistent, which may lead to the uneven stress distribution in the screw hole and affect the stability of the fastening force.
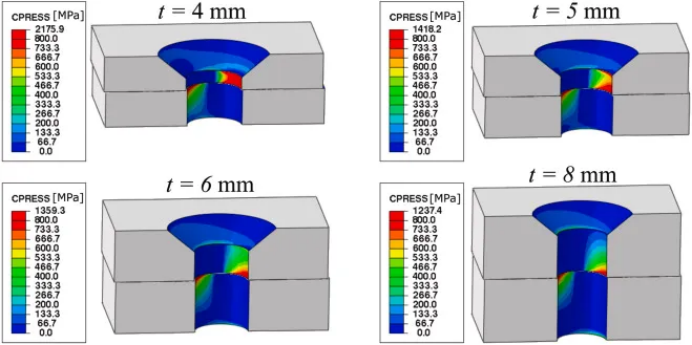
1.2 Concentration of thermal stress
Before and after the start of the equipment, the thermal stress is concentrated in local areas due to the sudden change of temperature difference, which is particularly unfavorable for the joint tightening force of bolts and screw holes:
The thread root is the area of stress concentration, and the high temperature expansion may cause the microcrack expansion of the material.
Thin-walled screw holes are more likely to lose the tightness of the thread coordination due to the local deformation caused by the temperature difference.
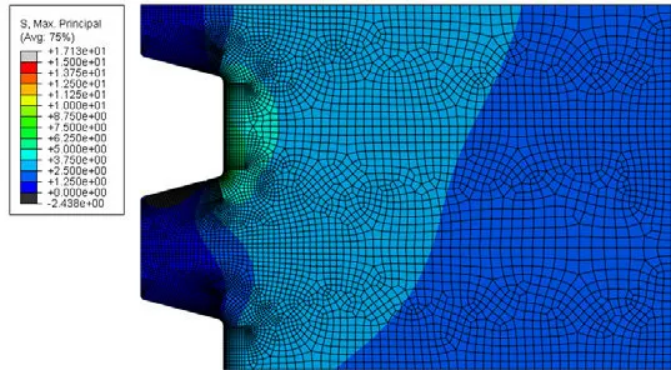
2. Specific impact of temperature difference on the tightening force
2.1 Increase or decrease of the tightening force
When the bolt expands faster than the screw hole, the fastening force increases, which may lead to the bolt creep or local yield of the material.
When the bolt contraction rate is faster than the screw hole, the fastening force is reduced, and loosening or connection failure may occur.
2.2 Effect of thermal fatigue and cyclic load
Repeated temperature cycles can cause thermal fatigue phenomenon and affect the service life of the fasteners:
The initiation thermal cycle of the material surface intensifies the development of micro cracks in the thread contact surface.
Bolt loosening defastening force changes accompanied by small slip accumulation may lead to bolt self-loosening.
3. Suggestions on the design and material selection for the temperature difference environment
3.1 Choose suitable materials
In the environment of the high thermal expansion matching material with a large temperature difference, the bolts with the thermal expansion coefficient close to the screw hole material should be selected.for instance:
Combination of steel and steel (e. g. 35 CrMo steel bolt and Q235 screw holes)
Titanium alloy bolts are used for lightweight equipment
High and low temperature resistance materials with high heat resistance and low temperature toughness, such as high nickel alloy (Inconel 718) or martensitic stainless steel (17-4 PH).

3.2 Optimize the design of screw holes and bolts
The circular Angle of the thread root is optimized to increase the circular Angle radius of the thread root, reduce the stress concentration, and improve the thermal fatigue resistance.
The wall thickness should meet the requirements of structural stability in the process of thermal expansion, to avoid the failure of the screw hole due to too thin.
3.3 Precise control of the pretension force
Critical to the design and control of pretension in temperature difference environment:
Use a performance-stable torque control tool under dynamic load.
The pretension design is optimized to be compatible with load changes caused by extreme temperature differences.
The influence of temperature difference environment on the fastening force of bolts and screw holes cannot be ignored. Through reasonable material selection, optimized design and surface treatment process, the performance and life of bolts in extreme environment can be significantly improved. In addition, combined with advanced thermal fatigue monitoring technology, the failure risk of bolt connection can be effectively predicted, so as to guarantee the long-term stable operation of the equipment.