Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 2 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-05-20 Origin: Site

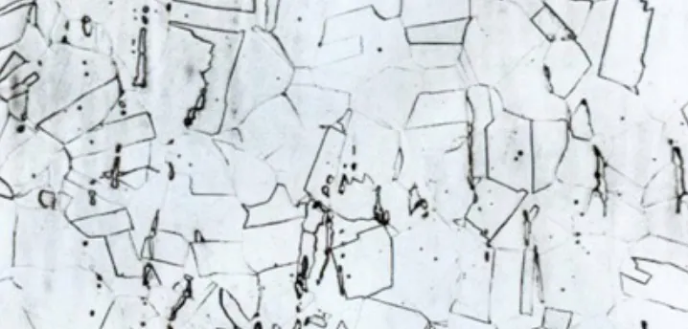
austenitic stainless steel
Austenitic stainless steel is mainly based on the face-centered cubic (fcc) lattice structure of austenite (γ phase). Common examples are 304,316, etc
Non-magnetic, mainly through cold working to strengthen it.
The mechanical properties of it can not be changed by heat treatment, but only by cold deformation.
Non-magnetic, good low temperature properties, easy formability and weldability are important characteristics of this type of steel.
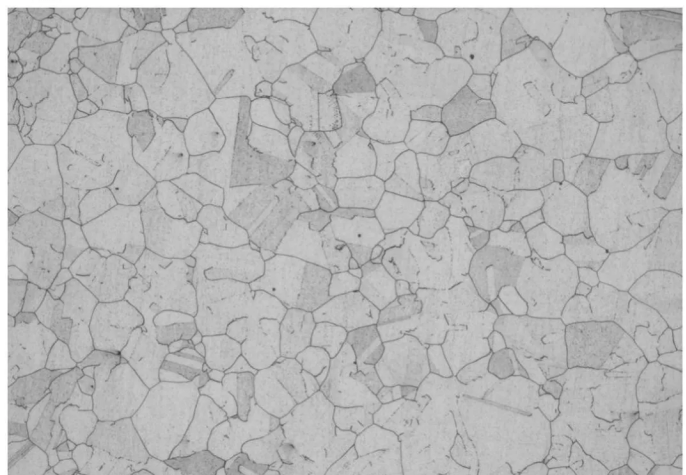

ferritic stainless steel
Ferritic stainless steel is a type of stainless steel that is mainly composed of ferrite under use. Common examples are 405,430, etc.
The stress corrosion cracking ability is superior to the austenitic series of stainless steel; it has strong magnetism at room temperature; it cannot be hardened by heat treatment, and has excellent cold workability.
Due to the stable presence of the ferrite phase, quenching cannot harden ferritic stainless steel. It exhibits maximum ductility and corrosion resistance in the annealed state. This steel is magnetic at room temperature. It features high thermal conductivity, low coefficient of thermal expansion, excellent oxidation resistance, and superior stress corrosion resistance, making it suitable for manufacturing components that withstand atmospheric, steam, water, and oxidative acid corrosion. However, this type of steel has drawbacks such as poor plasticity and significantly reduced weldability and corrosion resistance after welding, which limit its application. It is widely used in interior decoration, heavy oil burner components, household appliances, and home furnishings.
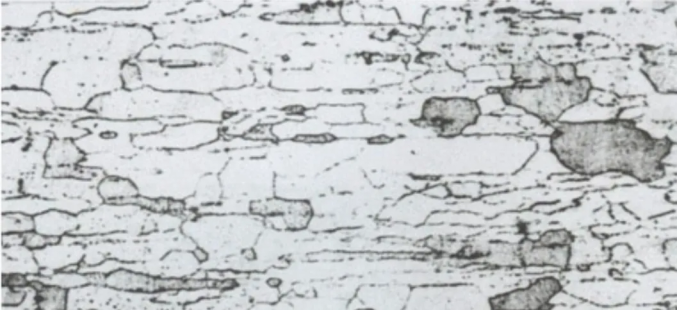
Martensitic stainless steel (M)
Martensitic stainless steel refers to the matrix is martensitic structure, commonly such as 403,416,420,440;
The main characteristics of martensitic stainless steel are that it has strong magnetism at room temperature, its corrosion resistance is not very outstanding, but its strength is high, and it is often used as high strength structural steel.
Strong hardening tendency, prone to cold cracking. In areas of the welded joint heated above 1150°℃, grain size significantly increases. Both excessively fast or slow cooling rates can cause joint embrittlement, leading to 475°℃ embrittlement. Intergranular corrosion is less likely, and 30Cr13,40Cr13,40Cr17Mo, and 95Cr18 have a stronger hardening tendency, generally not suitable for welding. Martensitic stainless steels have a clear transformation point and can be strengthened through quenching. With high chromium content, they have good hardenability, and their hardness, strength, and toughness can be adjusted over a wide range during tempering. High-carbon martensitic stainless steels have high hardness, making them suitable for both structural and tool applications. They are commonly used in components such as shafts, piston rods, pumps, valves, springs, and fasteners that require high mechanical properties, high hardenability, and resistance to nitric acid and organic acid corrosion.

Biphasic stainless steel refers to the ferrite and austenite each account for about 50%, generally less phase content is the least of 30% of stainless steel. This type of steel has the characteristics of austenitic and ferritic stainless steel. Commonly used: 2205.
Compared with ferrite, it has higher plasticity and toughness, no room temperature brittleness, significantly improved intergranular corrosion resistance and welding properties, while maintaining the 475℃ brittleness of ferritic stainless steel, high thermal conductivity and superplasticity.
Compared with austenitic stainless steel, the strength is higher and the resistance to intergranular corrosion and chloride stress corrosion is significantly improved.
The molybdenum-containing duplex stainless steel has good resistance to chloride stress corrosion at low stress.
Good corrosion fatigue and wear corrosion performance. Suitable for making pumps, valves and other power equipment under certain corrosive media conditions.
The comprehensive mechanical properties are good. It has high strength and fatigue strength.
Good weldability, small tendency to thermal cracking, generally no preheating before welding, no heat treatment after welding.
Compared with austenitic stainless steel, it has high thermal conductivity and low coefficient of linear expansion, which makes it suitable for lining equipment and producing composite plates. It is also suitable for making tube cores of heat exchangers, and the heat transfer efficiency is higher than that of austenitic stainless steel.
It should not be used in working conditions higher than 300℃.
Biphasic stainless steel can be used in oil refining, fertilizer, paper making, petroleum, chemical and other fields of heat exchangers, cold condensers and devices resistant to seawater, high temperature, concentrated nitric acid。

precipitation-hardening stainless steel
Stainless steel with austenitic or martensitic matrix, which is hardened (strong) by precipitation hardening (also known as aging hardening). Common examples are 630,660, etc.
Cemented hardened stainless steel combines the characteristics of these types of steel, with the corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steel and the high strength of martensitic stainless steel.
Cemented hardened stainless steel has the characteristics of high strength and good corrosion resistance. Its corrosion resistance is not only related to chemical composition, but also related to heat treatment, especially closely related to aging temperature.
Stainless steel with precipitated hardening is a kind of high strength stainless steel. In industrial applications, special attention should be paid to hydrogen cracking and stress corrosion cracking.
It is widely used in parts that require both high strength and high corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance, such as low-pressure turbine shaft, guide blade, working blade, fan frame, combustion chamber components of aviation engines, petrochemicals, ships, nuclear reactors, steam turbines, high-strength forgings, valves of high-pressure systems, etc.