Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 1 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-05-21 Origin: Site

oThis paper will focus on the key dimensions of gears, introduce the inspection methods such as the diameter of the division circle, tooth thickness and the length of the normal line, and give a systematic description of how to control the accuracy in actual manufacturing and maintenance.
oDefinition and detection method of division circle diameter
oThe division circle is the theoretical reference circle of gear meshing, and its diameter (d) is one of the most basic geometric dimensions in the design parameters.
otest method:
oGear measuring center (such as Klingelnberg, Gleason): can be automatically calculated by coordinate measuring head;
oUsing a grating profile projector or a three-coordinate measuring machine (CMM): the pitch is measured indirectly and converted;
oRoller micrometer method (suitable for small module gears): calculate and derive the external dimension between two teeth.
o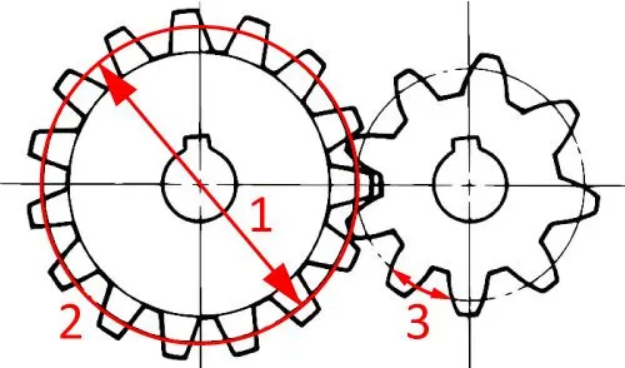
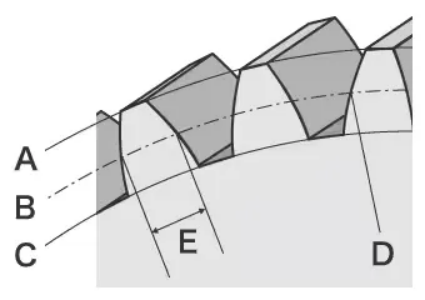
oThickness detection and control
oThe tooth thickness (s) refers to the width of a single tooth along the pitch circle of the gear, which directly affects the meshing clearance.
otest method:
oDent thickness gauge (denticle gauge): fast comparison of standard gears;
oRuler caliper + template method: compare the theoretical tooth shape;
oMicrometer + two rollers method: the tooth thickness is calculated by measuring the distance between two rollers;
oGear measuring instrument: can automatically generate comprehensive data such as tooth thickness distribution, tooth direction error and tooth shape error.
oControl points:
oAfter rough machining, a proper amount of allowance is reserved, and the final tooth formation or grinding is controlled to the tolerance;
oThe deformation after heat treatment is measured and corrected again.
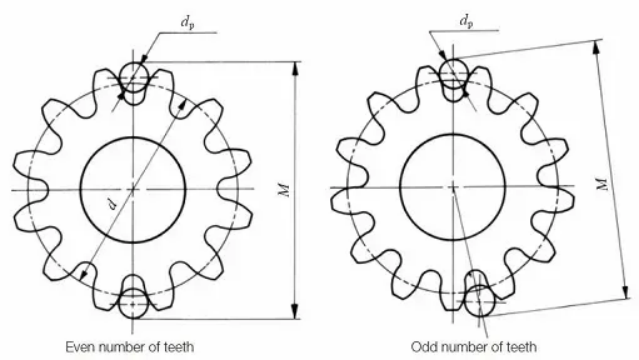
Method of measuring the length of public law line
Public law line (W) is an important parameter for cross-gear measurement of multiple teeth of gears, and it is one of the important means to control gear accuracy. It is especially suitable for the control of helical gears and shaped gears.
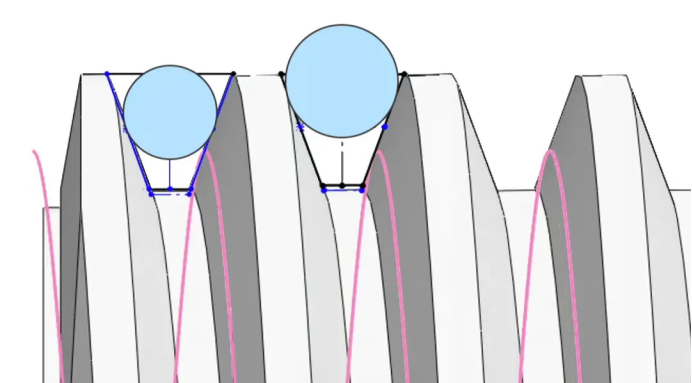 measuring method:
measuring method:
Use public law line measuring instrument (manual or automatic);
Use double-sided meshing instrument for cross tooth detection;
MMGear, Gleason The measurement system automatically analyzes the common normal error of multiple tooth positions;
Calculation formula reference standard: GB/T 10095, ISO 1328.
critical control point:
The measured number of teeth and pitch fit should comply with the standard recommendation;
The gap error of the calibrated probe should be within the allowable range;
The ambient temperature is controlled at 20℃ to reduce the influence of thermal deformation.
Shape and position tolerance detection and error correction
In addition to the size parameters, the shape and position accuracy of gears (such as tooth shape error, tooth direction error, radial runout, etc.) is an important standard for the final precision control, which is evaluated according to GB/T 10095-2008 standard or ISO 1328.

detection device:
Double-sided engagement instrument: can quickly detect the comprehensive engagement error;
Gear measurement center (three-coordinate system with gear module);
Circular runout measuring instrument (testing installation reference);
Surface profilometer: used for tooth surface roughness assessment.
Error correction strategy:
Add tooth profile modification to the gear grinding process;
The repetitive positioning fixture improves the processing consistency; after the heat treatment deformation evaluation, the fine grinding is reasonably grouped.

Precision control and quality closed loop system
In order to ensure the overall manufacturing quality of gears, it is necessary to establish a perfect closed-loop quality control system:
Raw material incoming inspection: hardness, structure, size preliminary inspection;
Process control: first piece inspection + patrol inspection + key process inspection;
Middleware size control card: establish process parameter file;
Final inspection: 100% detection accuracy level to determine whether it is qualified;
Traceability management: label number, certificate of conformity management, data archiving.

oStandard basis and measurement uncertainty assessment
oKey reference criteria:
oGB/T 10095 (equivalent to ISO 1328);
oJB/T 6141 General Technical Conditions for Gear Measuring Instruments;
oInterpretation of gear technical parameters ISO/TR 10064;
o JJG 507 Gear measuring instrument calibration specification.
oMeasurement uncertainty source:
otemperature shift;
oDetection equipment resolution;
opersonal error;
oProcessing base deviation.
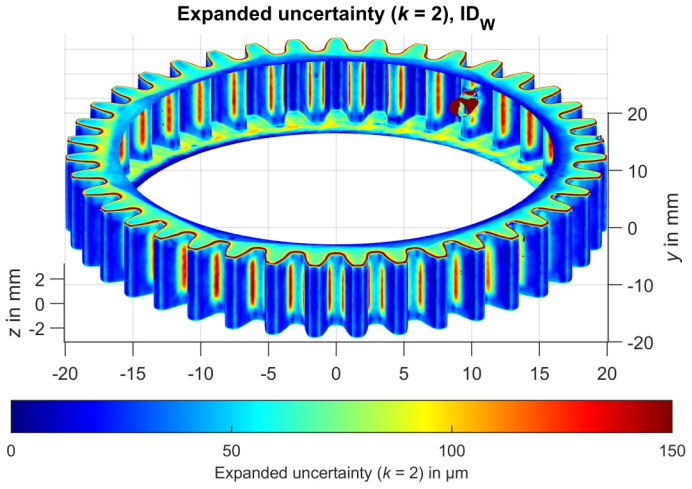
In the manufacturing and maintenance of high-precision gears, dimensional inspection and accuracy control run throughout the entire process. Especially in critical industries such as rail transit and aerospace, any dimensional error in gears can lead to unforeseeable consequences. Only by adhering to standards and relying on data can we ensure that gear quality is controllable, reliable, and safe.