Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 1 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-03-11 Origin: Site
In the gear transmission design, the pressure angle (Pressure Angle, α) is a key parameter, which directly affects the gear contact stress, transmission stability and bearing capacity. ISO 53 The standard specifies the commonly used pressure angle values, where 20 and 25 are the two most common pressure angle choices. So, in the practical engineering application, how to choose the appropriate pressure Angle according to the working conditions? This paper will deeply analyze the transmission characteristics of 20 and 25 pressure angle gear, and discuss the application of rail transit gearbox.
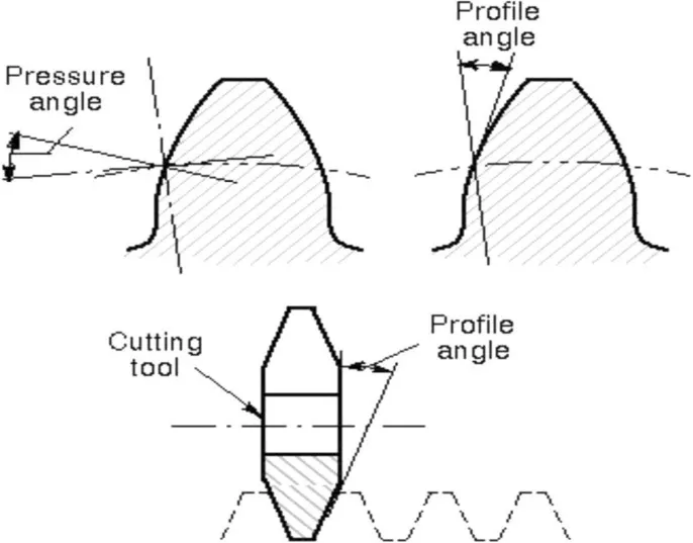
Basic concept of the pressure angle
The pressure angle α is the angle between the normal and the common normal of the gear engagement point.
The size of the pressure angle determines the direction of the gear transfer force:
A smaller pressure Angle (such as 20) will produce a large tangential force, improve the transmission stability, suitable for high precision, low noise occasions.

A large pressure angle (such as 25) will increase the radial force and improve the bearing capacity of the gear, suitable for high load conditions, such as rail transit drive system.
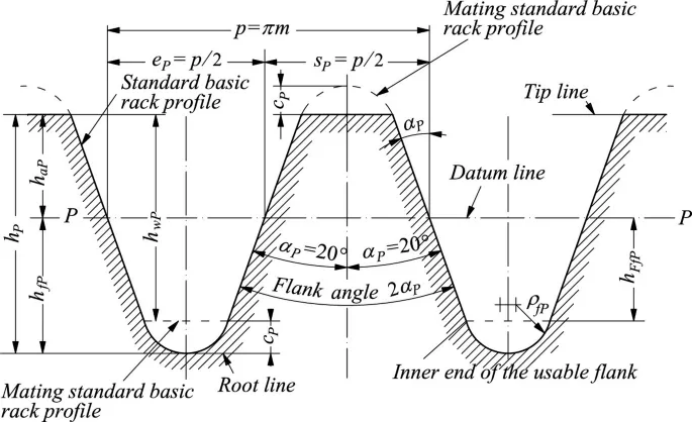
2. ISO 53 Standard provision for pressure angle
ISO 53 As the international gear standard, it specifies the matching relationship of gear module, tooth number and pressure angles, of which 20 and 25 are the most common standard pressure angles:
20 Pressure Angle (ISO 53 recommendation)
Suitable for the vast majority of industrial gear, such as machine tools, automobile gearbox, etc.
The gear profile is more balanced, with high transmission efficiency and low noise.
Moderate carrying capacity is suitable for moderate load application scenarios.
25 Pressure Angle (ISO 53 extended application)
Suitable for heavy load, high impact load of the gear system, such as rail transit gear box, mining machinery.
Increased the bearing capacity of the gear, but at the cost of a large radial load, the need to strengthen the bearing support.
It is suitable for space limited and high strength gear.
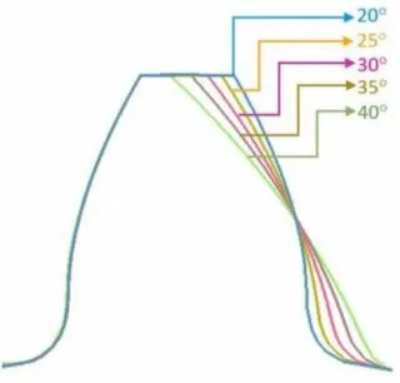
3. Selection analysis of 20 and 25
From the perspective of type selection, if the gear needs high precision, high stability, the 20 pressure angle is the best choice; if the gear bears heavy load and large impact load, the 25 pressure angle is more appropriate.
4. Application of pressure Angle in rail transit gearbox
In the rail transit gearbox, the gear not only needs high strength, but also ensures a long life and low noise, so the choice of pressure Angle is particularly critical.
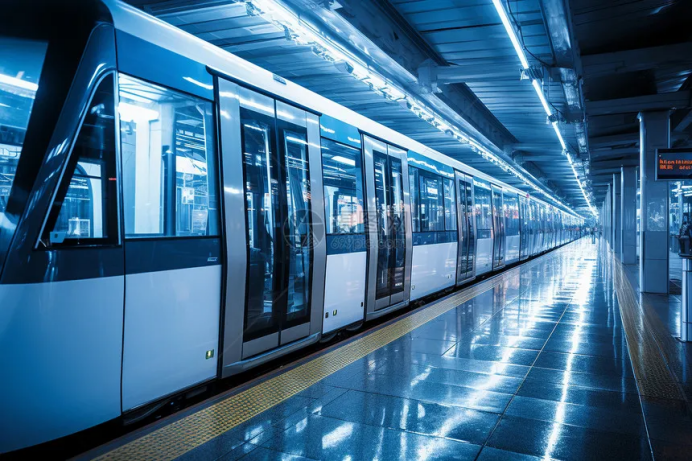
The subway gearbox usually adopts 20 pressure Angle to reduce the vibration noise and improve the operation stability, which is suitable for the comfort requirements of urban rail transit.

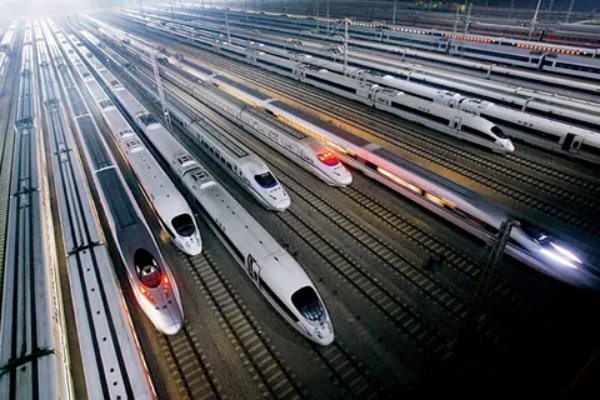
High-speed railway gearboxes usually use 20 or 22.5 pressure angles to balance the carrying capacity and transmission efficiency, while optimizing the durability of the gear.

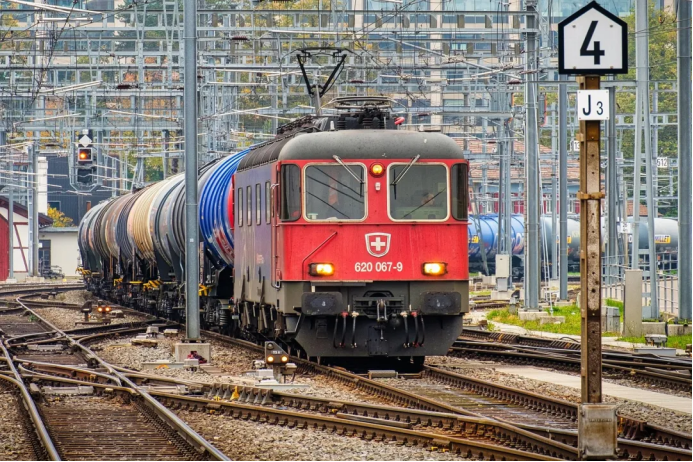
The gear box of heavy-duty freight train usually adopts 25 pressure Angle to improve the gear bearing capacity, enhance the gear impact resistance, and adapt to the long-term high-torque working environment.

5. Calculate the case analysis
Case 1: Effect of pressure angle on gear contact stress
It is known that the power of the gear transmission is 100kW, the gear modulus is 6mm, and the speed is 1800rpm, calculating the contact stress change at the pressure angles of 20 and 25 respectively.
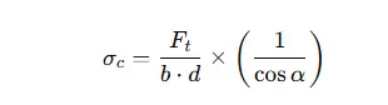
The calculation results show that under the same working condition, the contact stress of the pressure angle gear of 25 is about 12% higher than the pressure angle gear of 20, which means that the gear tooth surface needs higher wear resistance and stronger material support.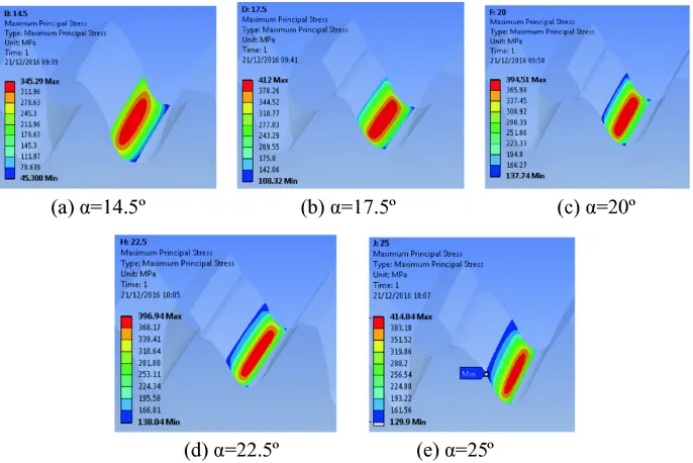
20 The pressure angle is suitable for most industrial gears, smooth transmission, low noise, and widely used in urban rail transit gearbox.
25 Pressure Angle is suitable for high load and high impact working conditions, such as heavy-duty rail train and mining equipment, but the bearing design should be strengthened.
20 or 25 is usually selected according to the operation requirements, which should be combined with load calculation, noise control, gear life and other factors.
In the engineering design, FEA simulation can analyze the force situation of different pressure angles, optimize the gearbox design, and improve the reliability of the transmission system.