Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 2 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-03-10 Origin: Site
1. Source of bearing noise and vibration
The noise and vibration of the bearing mainly come from the following aspects:
1. Manufacturing and processing errors
The geometric accuracy of the roller path and the rolling body is insufficient, such as the roundness error and the excessive ripple, which will lead to the increase of vibration when the bearing runs.
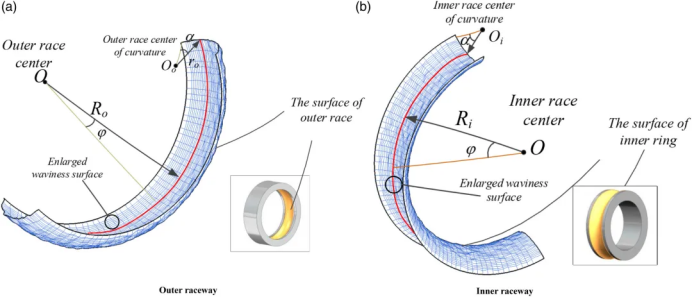
The internal gap of the bearing is too large or too small, which affects the force state of the rolling body and produces abnormal noise.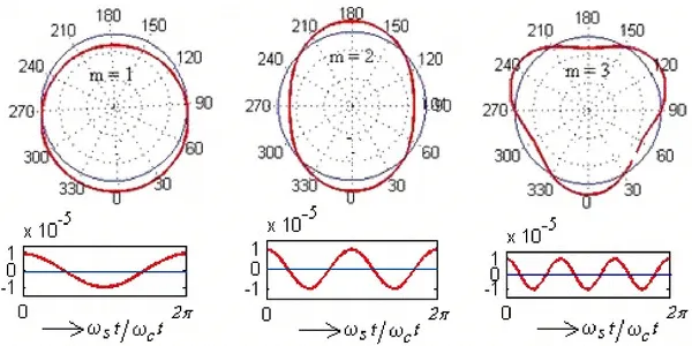
2. Poor lubrication
Insufficient lubricant or decreased quality of lubricant will lead to increased friction when the bearing runs and produce high-frequency noise.
Ununiform grease distribution may cause local overheating or friction changes, resulting in periodic vibration.

3. Assembly problems
Bearing installation is eccentric or the pretightening force is too large, resulting in uneven bearing rolling and causing vibration and noise.
The coordination tolerance of bearing and shaft or bearing seat is too loose or too tight, which affects the operation stability.

4. Poor operating conditions
Overload or impact load will cause the abnormal vibration and noise of the bearing.
External pollutants (such as dust, moisture) enter into the bearing interior, causing foreign body friction noise.

2. Type and influence of bearing noise
According to the source and spectral characteristics of the noise, the bearing noise can be divided into the following categories:
1. Rolling body noise (Rolling Noise)
Genered by the interaction between the rolling body and the rolling path, usually medium and high frequency noise.
Impact: accelerate the bearing surface fatigue, affect the service life.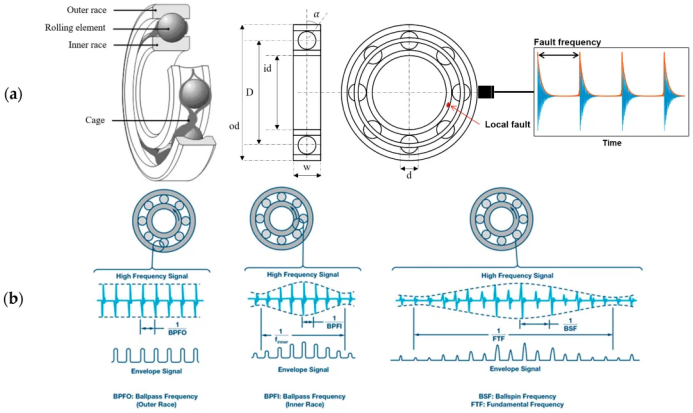
2. Impact noise (Impact Noise)
Due to the violent impact between the rolling body and the roller path, it usually occurs when the pretightening force is too large or the bearing gap is not reasonable.
Impact: It may cause internal damage to the bearing and aggravate the wear.

3. Lubrication noise (Lubrication Noise)
Due to the rupture of the lubricating oil film or the insufficient supply of lubricant, the contact friction between the rolling body and the roller path increases, causing irregular noise.Impact: It may cause local overheating of the bearings, resulting in lubricant deterioration.
4. Electromagnetic noise (Electromagnetic Noise)
Mainly in motor bearings, the small discharge generated by current through the bearing leads to metal surface damage and high frequency noise.Impact: Electrical erosion may lead to bearing failure and affect the long-term stability of the equipment.
3. Effect of lubrication mode on bearing noise
The lubrication modes of bearings are mainly divided into grease lubrication and oil lubrication. Different lubrication modes have different effects on bearing noise and vibration.
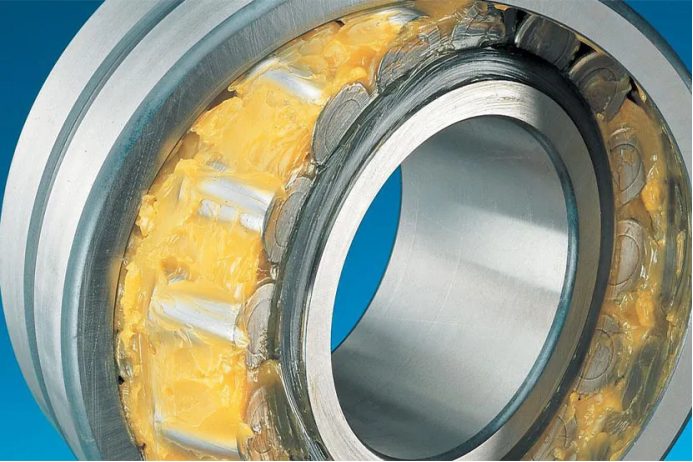
1. Fat lubrication (Grease Lubrication)

2. Oil lubrication

Characteristic lubricating oil can flow quickly, form a stable oil film, effectively reduce the bearing internal friction noise.
merit
Suitable for high-speed bearing to reduce temperature rise and improve heat dissipation performance.
The lubrication effect is more stable, reducing vibration and wear.
shortcoming
Need for additional lubrication system and high maintenance costs.
4. Detection method for bearing noise and vibration
To ensure the normal operation of the bearing, the noise and vibration detection can be performed by using the following methods:
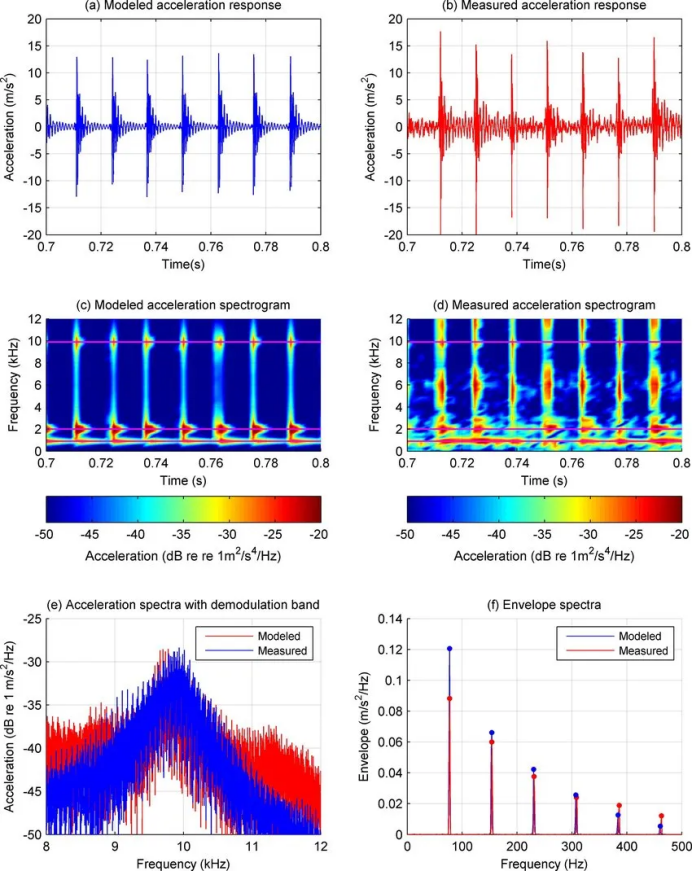
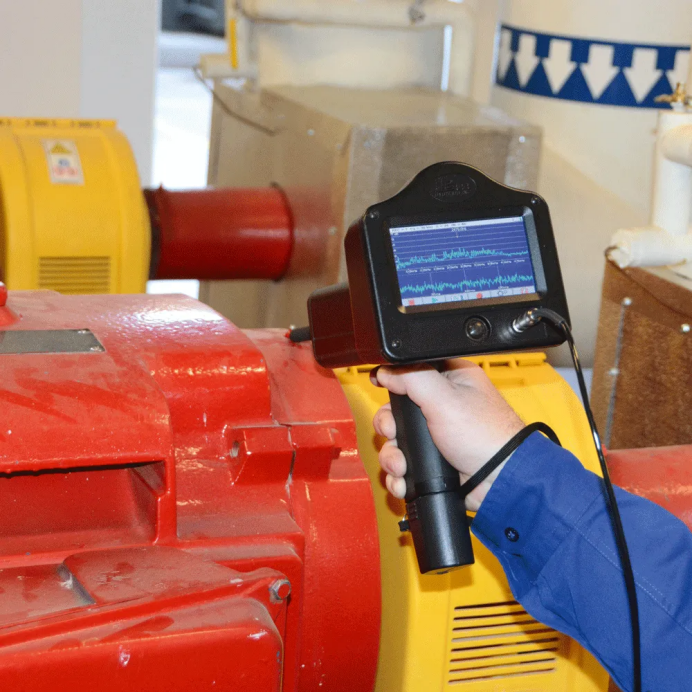
1. Vibration Analysis (Vibration Analysis)
Monitor the vibration signal of the bearing by the acceleration sensor to analyze the running state of the bearing.It is suitable to identify the early damage of bearing, such as roller path point erosion, rolling body defect, etc.

2.Spectrum analysis (Spectrum Analysis)
The Fourier transform (FFT) is used to analyze the vibration spectrum of the bearing and determine the fault type.
Accurately locate bearing faults by characteristic frequency (e. g. inner ring, outer ring, holder, rolling body fault frequency).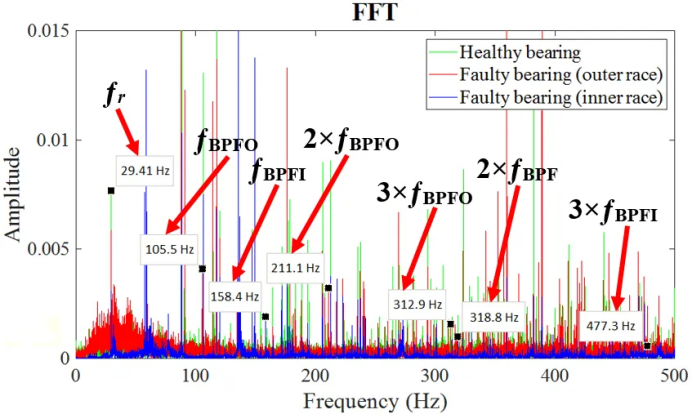
3. Stestethoscope Detection (Stethoscope Test)
The operating noise of the bearing is directly monitored by the mechanical stethoscope.Suitable for rapid diagnosis, but cannot quantitatively analyze the fault severity.
5. How to reduce the bearing noise and vibration?
1. Improve the manufacturing accuracy
Choose high precision bearing to reduce the shape error of rolling body and rolling way.
Control the internal bearing clearance to reduce the additional vibration source.
2. Optimize the lubrication scheme
Select the proper lubrication method and lubricant to ensure adequate and uniform lubrication.
Oil lubrication is preferred at high speed to reduce friction and temperature rise.
3. Correct installation and maintenance
Ensure the bearing installation coaxiality to avoid excessive assembly stress.
Check the lubricant status regularly and clean up the internal pollutants of the bearing.