Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 3 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-04-08 Origin: Site
Sliding fit and rolling fit are two common types of motion, widely used in components such as guides, bearings, pistons, sliders, and couplings. Although both fall under the category of "motion fits," their structural principles, load characteristics, and design requirements are entirely different, especially in terms of tolerance settings, which must be scientifically matched according to specific functions.
In this issue, we will delve into the key considerations of sliding and rolling fits in tolerance design, as well as how to set tolerances properly to ensure that equipment does not loosen or get stuck during movement.
What is sliding fit and rolling fit?
✅ easy push fit
Sliding fit is a form of relative motion that relies on direct contact between surfaces. Typical examples are reciprocating sliding of pistons in cylinders, sliding of guide blocks, etc.
✅ Rolling fit (Rolling Fit)
Rolling coordination through the middle rolling elements (such as ball, roller) to reduce friction, the typical representative is the rolling bearing and shaft or seat hole coordination.
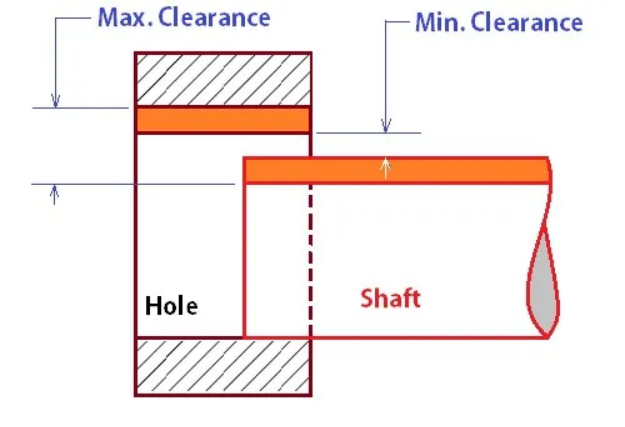
2. Tolerance design principle for the sliding fit
The design goal of the sliding fit is to slide smoothly without any significant clearance or shaking. Too tight will jam, too loose will affect the accuracy.
⚠ matters need attention:
Temperature compensation: if the material of slide and guide rail is different (such as copper and steel), the influence of thermal expansion should be considered and the gap should be enlarged appropriately enlarged.
Lubrication treatment: the lubricating oil film space shall be reserved (such as 0.002~0.005mm).
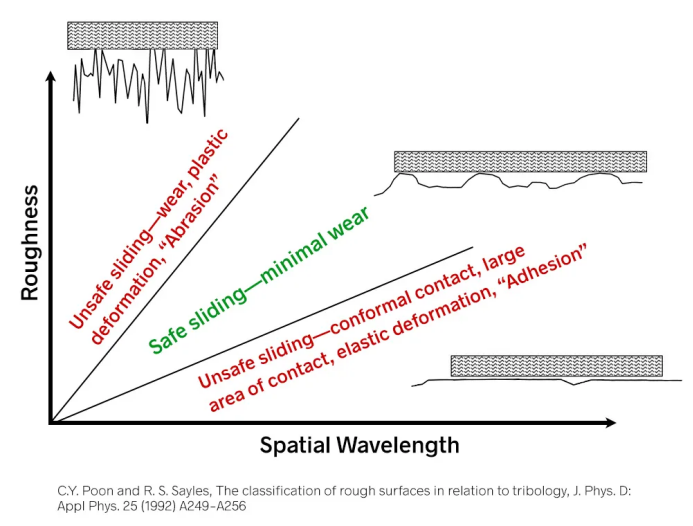
Processing process matching: it is recommended to use grinding or fine milling to ensure the matching surface roughness, Ra 0.8 μ m.
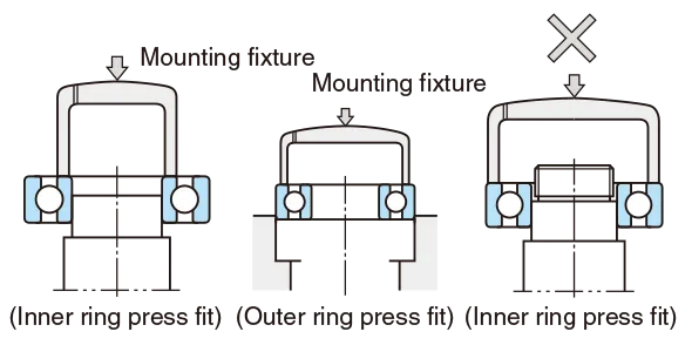
3. Tolerance design principle for rolling fit
Rolling cooperation is mainly used in bearing installation, the goal is to ensure that the bearing inner and outer ring is fixed and does not rotate in the work, but without excessive interference.
⚠ Key issues of rolling cooperation:
An surplus fit must be used when rotating the bearing ring to prevent skid relative to the shaft (creep).
When the outer ring is fixed in the seat hole, it is recommended to use slight clearance matching to prevent heat swelling stuck.
The installation method (cold, hot and pressing) has a great impact on the coordination effect, and the interference value should be reserved in the design.
4. Common misunderstandings and corrective suggestions in tolerance design
Actual case reference: coordination design of guide rail slide and rolling bearing seat
✔ Case 1: CNC machine tool sliding guide rail
Material: grey cast iron + copper slide block
Coordination: H7 / e7
Features: medium slip resistance, can absorb micro vibration, suitable for medium and low speed and high precision processing
Case 2: Motor rotor rolling bearing installation
Material: 45 steel shaft + 6205 deep groove ball bearing
Coordination: h6 / n6
Assembly method: quick installation after hot assembly (bearing heating to 120℃)
✅ Sliding coordination should pay attention to the clearance and lubrication, and the tolerance setting should take into account the thermal expansion and surface roughness.
✅ Rolling cooperation is to prevent rotation slip and reasonable interference, the tolerance must be distributed in the direction of shaft bearing force.
✅ All the coordination design should be adjusted according to the working conditions, combined with the temperature, material, assembly method, life requirements and other comprehensive judgment.