Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 4 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-04-15 Origin: Site
The effect of gear type on noise
Different types of gears, due to their different geometric characteristics, will have different forms of meshing process. For example: under the same load and speed conditions, through many application cases can be found that the noise of helical gears can be 3~10dB lower than that of straight gears;
The influence of pressure Angle on gear noise
To transmit a certain power, F must be kept constant. If the pressure angle a is increased, the normal force Fn on the tooth surface must also increase. This will result in an increase in the pitch line force and meshing force on the actual tooth surface with friction, leading to an increase in vibration and noise levels. Although the error in the center distance of gears does not affect the accurate meshing of involute teeth, its variation causes periodic changes in the working pressure angle. For example, eccentricity of the gear on the shaft will change the rotational frequency of the gear to a variable center distance, which will inevitably modulate the frequency of the vibration and noise in gear transmission. The amplitude of this modulation depends on the size of the eccentricity.
The influence of overlap degree on gear noise
The number of teeth varies to different degrees when transmitting the load. Thus, the engagement impulse along the direction of the engagement line will be generated at the moment of entering and disengaging the meshing, resulting in torsional vibration and noise.
If the instantaneous average number of teeth is increased, that is, if the overlap is greater, the load can be distributed over more teeth, reducing the unit pressure on the tooth surface. This, in turn, minimizes tooth deformation and improves the impact during engagement and disengagement, thereby reducing torsional vibration and noise in gear transmission. Application cases show that when the overlap increases from 1.19 to 2.07, noise is reduced by 4dB at 1000rpm and by 6dB at 2000 rpm.
For helical gears, the overlap can be increased by changing the helix angle β and tooth width b, and it can greatly exceed that of spur gears. However, the helix angle should not be too large, otherwise it will cause axial vibration. Increasing the number of teeth, increasing the tooth tip height coefficient or reducing the pressure angle can all increase the overlap, reduce vibration and noise.
The influence of gear precision on noise
Gear noise is greatly affected by gear accuracy. An important part of reducing gear noise is to improve gear accuracy. For gears with extremely low accuracy, any other noise reduction measures will often be futile. Among the single errors, the two most influential are pitch (base or circumference) and tooth shape:
1. Tooth pitch:
The noise increases or decreases in direct proportion to the base error. When the speed increases or the load increases, the gradient of the noise increases or decreases. Moreover, in one revolution of the gear, even if there is a large pitch error, the noise also increases significantly.
2. Tooth shape:
Only the size of the tooth error can not be judged to its effect on noise, the important thing is the shape of the tooth error, for example, the "concave" near the node will increase the noise a lot.
3. Radial runout of gear ring
Due to the modulation of sound, there are sometimes multiple screaming sounds in gear noise, and eccentricity causes continuous changes in the circumference, resulting in long cycle noise related to the rotation frequency of the tooth cycle. Human ears are very sensitive to this, especially at high speeds.
4. Tooth surface roughness
Gear error has a great influence on noise, especially in the field of high engagement frequency, the sound pressure level is quite high, and the sound is unpleasant.
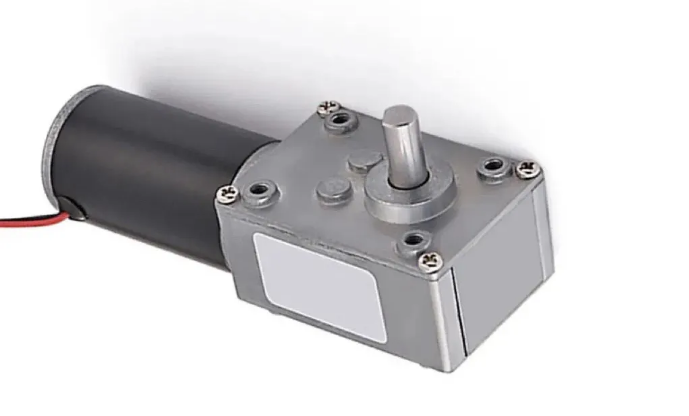
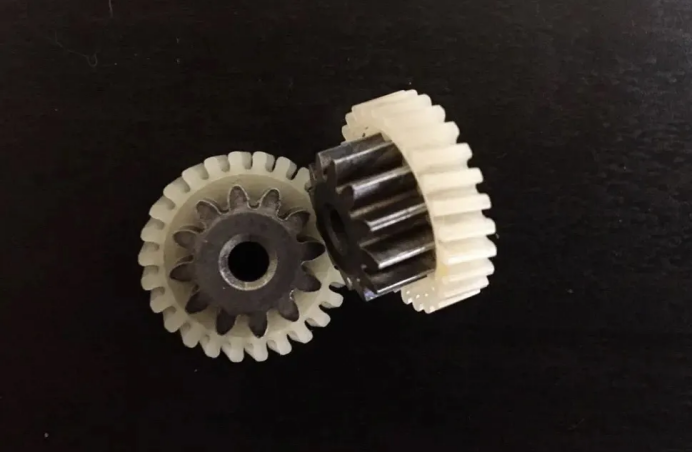


For the application of plastic gears in the first stage of speed reduction gearboxes for electric baby swings and electric rocking beds, as well as various types of speed reduction gearboxes, We can help you solve the following issues: 1.POM and PA66 gears have relatively high noise levels, insufficient wear resistance, and fatigue resistance, and POM gears are prone to tooth breakage. 2.PA12 and TPEE gears are too soft with low torque and insufficient wear resistance, and their torque decreases rapidly above 60 degrees Celsius. 3.POM and PA66 gears lack corrosion resistance, and POM gears are prone to wear and powdering when used in injection-molded functional components. 4. Nylon 46 gears have inadequate noise reduction properties and are significantly affected by moisture. As a strong and wear-resistant engineering plastic, Z33 material stands out in gear applications for its: wear resistance, silence, corrosion resistance, strength, and insensitivity to moisture. Typical successful applications of Z33 material include micro and mini speed reduction gearboxes, electric actuators, EPS gears for automotive steering systems, massage device gears, gasoline engine cams, mid-drive motor gears for electric-assist bicycles, and electric shavers, among other transmission gears.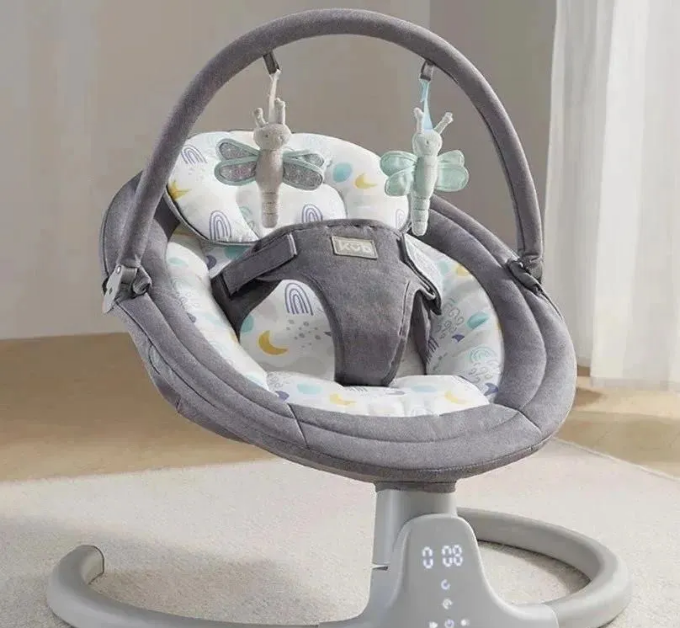
The source of noise generated by the reduction gearbox
1. The gear runs too fast
The vibration speed of the gear running is too fast, mainly because the frequency of the gear transmission is too fast, resulting in the vibration frequency between the gears is too fast. The vibration speed of the gear running will affect the vibration frequency and produce noise.
2. Load impact brings about gear vibration
Here, the gear transmission is viewed as a vibrating spring system, with gears naturally becoming part of this system. When the gears are subjected to different levels of load, the frequency and direction of vibration will vary, often forming a circular oscillation. Coupled with the gear's inherent noise reduction capabilities, this results in smooth, non-shaking noise.
3. Noise generated by resonance
Resonance can produce noise, which everyone knows. As the primary method of operation in production workshops, gear transmission naturally experiences resonance during its operation. The resonance caused by gear transmission is based on vibrations generated by the poor rigidity of gears and the friction between gears, both occurring at the same vibration frequency. At this point, their interaction easily leads to resonance, resulting in noise.
4. The surface finish of some gears is insufficient
As is well known, if two objects are smooth, the vibration generated during mutual friction will be small, with low vibration frequency and high-frequency waves, naturally resulting in less noise. However, many gear surfaces are too rough, leading to large friction areas and high vibration frequencies when they rub against each other, thus producing more and greater noise.
5. Lack of proper lubrication support
In gear maintenance and noise reduction, not only can good lubricants reduce friction and vibration between gears, but their proper use is also a crucial method for lowering and reducing noise. Traditional lubrication methods involve increasing the amount of lubricant on the gear surface to reduce friction during operation, but this approach has minimal effect on noise reduction. From the perspective of foreign practices in gear maintenance and noise reduction, greater emphasis is placed on lubrication methods, which involve thoroughly injecting lubricant into the gear interior to reduce noise.
6. The material selection of the gear is unreasonable
If more flexible wear-resistant materials are used to replace the harder wear-resistant materials, the noise of gear transmission can be reduced to a certain extent. For example, in the application of plastic gears, the wear-resistant and silent gear engineering plastic Wintone Z33 is used instead of the conventional POM. Z33 material can not only improve the wear resistance and fatigue resistance, but also help to greatly reduce the noise of gear transmission.
In the past dozen years, nylon 12 or TPEE materials have often been used to solve noise issues. However, while using PA12 to address noise problems, another issue emerged: PA12 and TPEE gears can withstand much less torque than POM gears. When the motor temperature exceeds 60 degrees Celsius, the torque drops too quickly. Additionally, the high cost of PA12 limits some applications. Z33, a specialized engineering plastic for wear-resistant and silent gears, offers improved wear and fatigue resistance compared to nylon 12. It also exhibits enhanced rigidity, toughness, and vibration damping properties. In many applications of small and micro gearboxes and planetary gearboxes, Z33 material has proven to be effective
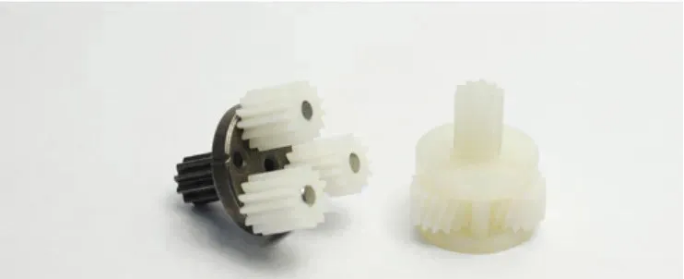
In the application of the first and second plastic planetary gears in the electric cleaning brush planetary plastic gearbox, wear-resistant and silent gear special material can help you solve the problem that traditional POM, nylon and soft rubber TPEE materials are difficult to achieve a good balance of high torque, low noise and good wear resistance and fatigue resistance.