Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 2 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-06-23 Origin: Site
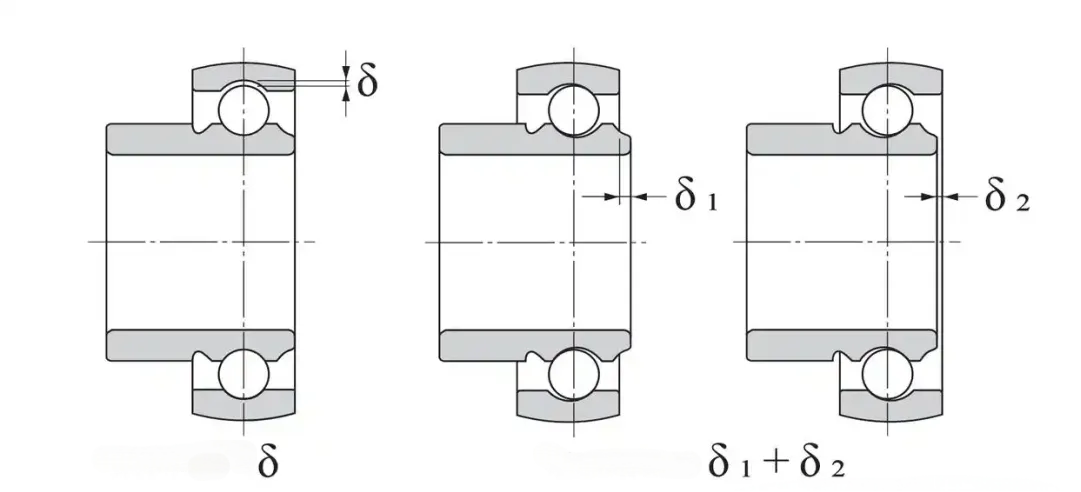
The clearance of a bearing is a critical parameter in its design and application, directly impacting the bearing's lifespan, noise levels, temperature rise, and load-carrying capacity. If the clearance is too small, it can lead to overheating, jamming of the rolling elements, and increased friction wear; if the clearance is too large, it can increase vibration and noise, reduce the load-bearing area, and decrease the bearing's load-carrying capacity. I. Bearing Clearance: 1. Definition of Bearing Clearance: There is an inherent gap between the inner ring, outer ring, and rolling elements of a rolling bearing, allowing for relative movement between the inner and outer rings. In the absence of external forces, when one ring is fixed, the other ring can move freely along the radial and axial directions of the bearing. Ø Radial Clearance: The relative movement of the inner ring and outer ring in the radial direction. Ø Axial Clearance: The relative movement of the inner ring and outer ring in the axial direction. Ø Clearance Types: C0~C5: Standard clearance grades (CN is the standard grade, with higher numbers indicating greater clearance). Special Clearance: Such as C9 (greater than C5), C1 (less than C0), etc.
2. Based on the bearing's condition, clearance can be categorized as follows: Original clearance: the clearance of the bearing in its free state before installation. Installation clearance: the clearance after the bearing is installed with the shaft and bearing housing but before it starts to operate. Due to interference fit, an increase in the inner ring size, a decrease in the outer ring size, or both, the installation clearance is typically smaller than the original clearance. Working clearance: the clearance of the rolling bearing during operation. The working clearance changes due to the thermal expansion of the inner ring during operation and the elastic deformation between the rolling elements and the raceway under load.
Second, the hazards of improper clearance: The working clearance is a critical performance indicator for rolling bearings, directly affecting load distribution, vibration levels, noise generation, friction torque, and service life. An inappropriate working clearance can cause serious damage to equipment. 1. Insufficient bearing working clearance: Bearing overheating and increased noise. When the working clearance is too small, it may result in negative clearance (overrun) during actual operation, leading to an increase in friction torque, which generates significant heat and can cause the bearing to overheat and fail. This is because a small clearance hinders the smooth lubrication of the rolling elements and the inner and outer rings, leading to wear, seizure, and even cracking of the bearing, ultimately resulting in its failure. 2. Excessive bearing working clearance: Increased vibration and poor positioning accuracy. An excessively large clearance reduces the bearing's internal load-bearing area, increases contact surface stress, and shortens its service life. It also decreases the bearing's operational precision, increases vibration, and raises noise levels. Third, selection of clearance: When selecting bearing clearance, first ensure that the clearance meets the performance requirements of the bearing under specific operating conditions. Second, the selected clearance should ensure the bearing's long-term stable operation (the bearing is subjected to radial and axial forces during operation). Additionally, factors such as the type, size, and fit of the bearing must be considered to determine the most suitable clearance.
1. Clearance grade comparison table (based on ISO 5753)
| Clearance grade | Applicable bearing type, | typical application scenario |
| C2 | Less than CN (tight clearance) | High precision, low vibration (such as precision instruments) |
| CN | Normal clearance (default grade) | General operating conditions (default selection) |
| C3 | greater than CN | High temperature or interference fit (e.g. motor, gearbox) |
| C4/C5 | Greater clearance | Extreme high temperature or special mating requirements |
Standard clearance (such as C0, C2, C3, C4, C5): the value increases in sequence, and should be selected according to the working conditions:
ØC3: commonly used in motors and gearboxes (medium load, temperature change).ØLarge clearance (C4/C5): high temperature or inner/outer ring interference fit scenario.
Basic groups of bearing selection
Large clearance groups are suitable for situations where the interference fit between the inner and outer rings is significant, or there is a large temperature difference between the inner and outer rings. They are also ideal for deep groove ball bearings that need to withstand high axial loads, improve self-aligning performance, increase the bearing's maximum speed, or reduce friction torque. Small clearance groups are ideal for applications requiring higher rotational accuracy, strict control of the shaft displacement in the housing bore, and reduced vibration and noise.
Calculation of clearance
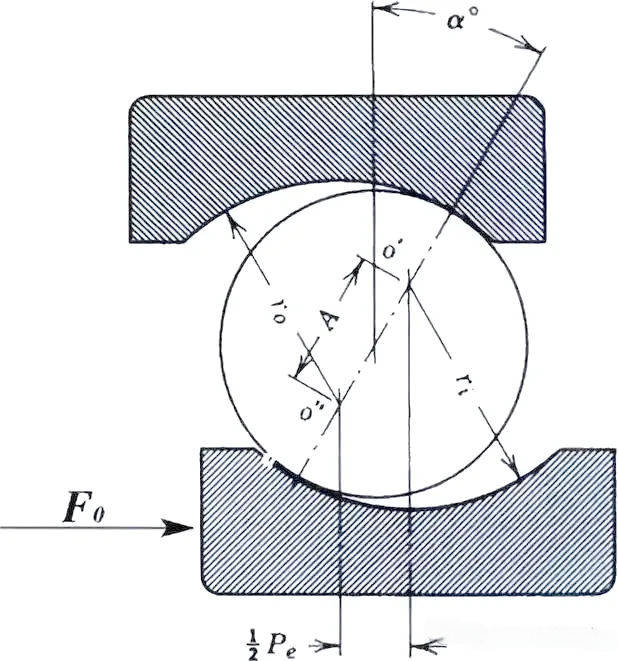
ØOverfitting: The overfitting between the inner ring and the shaft will reduce the radial clearance, so the compensation amount should be calculated in advance.
ØExperience formula: interference × 0.6 ≈ clearance reduction (e.g., interference 0.05mm → clearance reduction about 0.03mm).
ØTemperature effect: when running, the inner ring temperature is higher than the outer ring, so a thermal expansion clearance should be reserved.
The initial clearance and working clearance can be calculated using the formula δff = δ - (δf + δ), where δff represents the effective internal clearance (in millimeters), δ represents the bearing internal clearance (in millimeters), δf is the clearance reduction due to interference (in millimeters), and δ is the clearance reduction caused by the temperature difference between the inner and outer rings (in millimeters).
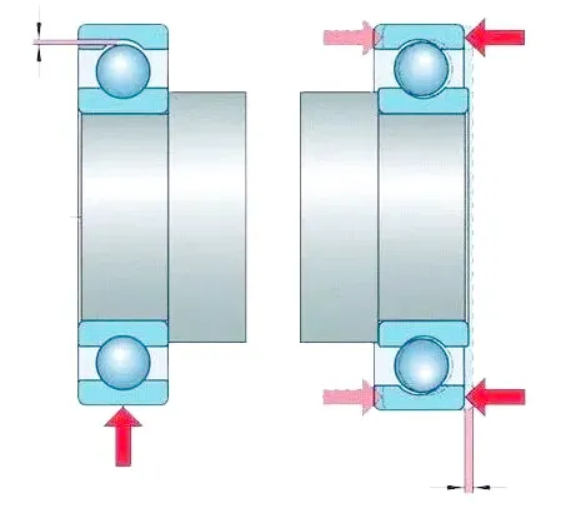
Clearance detection can be measured by using tools such as gap gauge, percentage gauge, micrometer, etc., or the finger inspection method and rotation flexibility inspection method can be used for preliminary judgment. When measuring, ensure that the bearing is unloaded and avoid impurities entering. 1. Radial clearance measurement feeler gauge method
a. Secure the outer ring and manually move the inner ring radially. b. Use a feeler gauge to measure the maximum clearance between the inner ring and the outer ring raceways (for large self-aligning bearings). Percentage gauge method a. Secure the percentage gauge probe perpendicular to the outer ring of the bearing. b. Move the inner ring up and down, and record the pointer swing range (accurate to 0.01mm). 2. Axial clearance measurement Sensory method Use your fingers to check the axial clearance of the rolling bearing, which is suitable for situations where the shaft end is exposed. When the shaft end is enclosed or cannot be checked with your fingers due to other reasons, you can check if the shaft rotates smoothly. Measurement method Use a feeler gauge to check, following the same procedure as checking radial clearance with a feeler, but the axial clearance should be calculated as c=λ/(2sinβ) c—— axial clearance, mm; λ—— thickness of the feeler gauge, mm; β—— bearing cone angle, (°). Percentage gauge method a. Secure the outer ring and push the inner ring axially. b. The difference in the percentage gauge reading is the axial clearance. Dial gauge method Use a crowbar to move the shaft to its two extreme positions, and the difference in the dial gauge reading is the axial clearance of the bearing. However, the force applied to the crowbar should not be too strong, as this can cause elastic deformation of the housing, even if the deformation is minimal, it can affect the accuracy of the measured axial clearance.