Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-01-24 Origin: Site
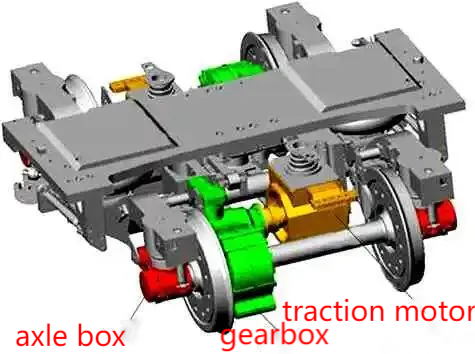
In the modern rail transit and mechanical equipment, the bearing is the key component in the transmission system, and its performance directly affects the operation efficiency and safety of the equipment. However, the bearing may fail for many reasons during operation, and the vibration signal is one of the early warning signals of the bearing failure. Through vibration monitoring and data analysis, the running state of the bearing can be effectively identified, potential problems can be found in advance, the risk of accidental shutdown can be reduced, and the stable operation of the equipment can be guaranteed. This paper will discuss the characteristics of bearing vibration, the vibration mode of common faults and the application of vibration monitoring in fault prediction.
1. Source and characteristics of bearing vibration
1. The main source of bearing vibration
The rolling body and the roller channel contact the rolling body when rolling on the roller path will inevitably produce vibration, which is the main source of bearing vibration.
Incorrect installation with assembly error or improper coordination of bearing with shaft and bearing seat will cause vibration.
Ununeven load distribution or impact load of the external load fluctuations can cause increased vibration.
Poor lubrication: Insufficient lubricating oil film or deterioration of lubricating grease will aggravate friction and cause vibration.

2. Characteristics of the vibration signals
The bearing vibration signal usually shows periodic or random vibration, and its spectral characteristics can be used to judge the running state of the bearing:
The base frequency and harmonic wave with low amplitude are mainly in the normal operating vibration frequency spectrum.
Spiking, high frequency signals or irregular fluctuations in the fault state vibration spectrum indicate a possible abnormality of the bearing.
2. Vibration mode for common faults of bearings
1. Fatigue peeling off
Description of small peeling of the roller path or rolling body surface due to material fatigue.
Vibrational features in the vibration frequency spectrum appear as periodic high-frequency pulses, accompanying a specific fault frequency.
Common position inner ring, outer ring, or rolling body.
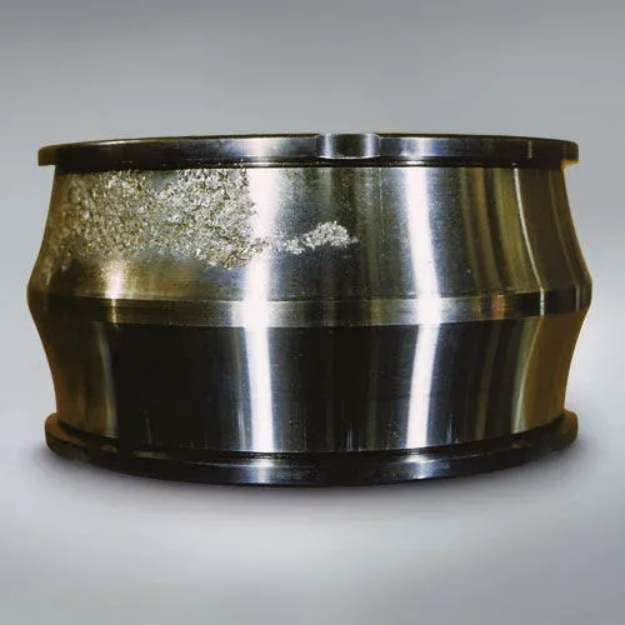

2. Point erosion
Describe pits or corrosion marks on the surface of the roller due to poor lubrication or excessive load.
Vibration features periodic vibration signals, with irregular high-frequency components.
Common location raceway surface.
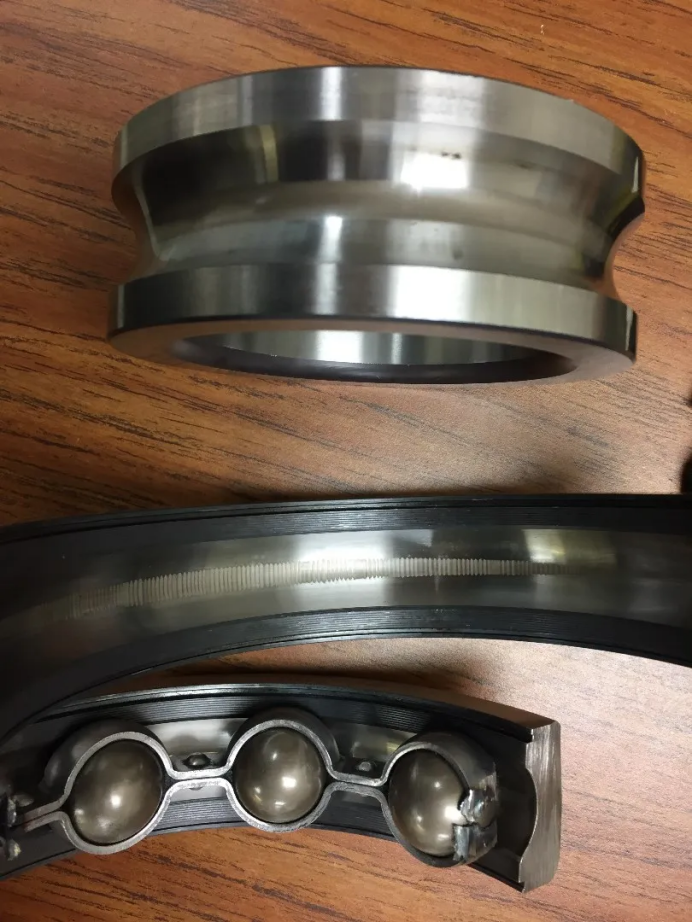

3. The holder is damaged
Description holder fracture or deformation affects the distribution of rolling body.
Vibration feature low frequency vibration is intensified, and irregular shock waveforms may appear in the vibration signal.
Common position holder contact parts.

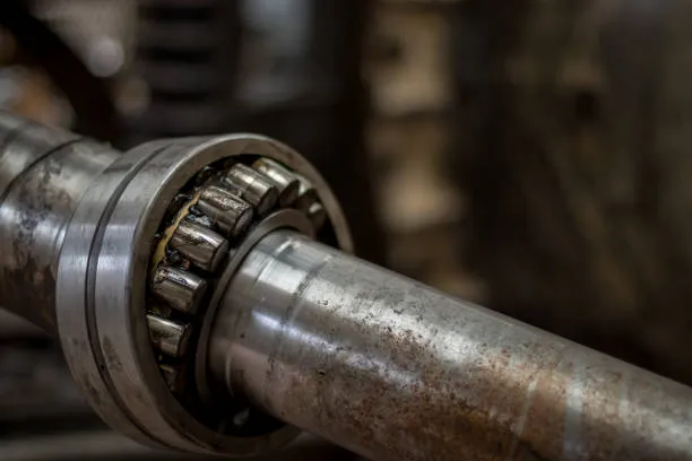
4. Poor lubrication
Describe insufficient lubricant or lubricant deterioration.
High-frequency noise with continuous vibration characteristics, and random high-frequency components appear in the vibration spectrum.
Common position rolling body and roller channel contact surface.

3. Vibration monitoring technology and fault prediction method
1. Basic technology of vibration monitoring
Acceleration sensor is used to capture vibration signals in bearing operation and record parameters such as acceleration, speed and displacement.
Spectral analysis transforms the time domain vibration signal into the frequency domain signal and identifies the fault type by analyzing the spectral features.
Demodulation to extract the shock components in the vibration signal and accurately locate the bearing fault frequency.

2. Data analysis method for fault prediction
Characteristic frequency analysis The fault frequency of the bearing is closely related to its geometric size and rotation speed, including the inner ring fault frequency, the outer ring fault frequency, the rolling body passage frequency, etc.
Trend analysis Through long-term monitoring of vibration signal analyzes the changing trend of vibration amplitude and predicts the deterioration degree of bearing.
Artificial intelligence technology combines machine learning algorithms (such as support vector machine, neural network) to predict bearing faults based on historical data.
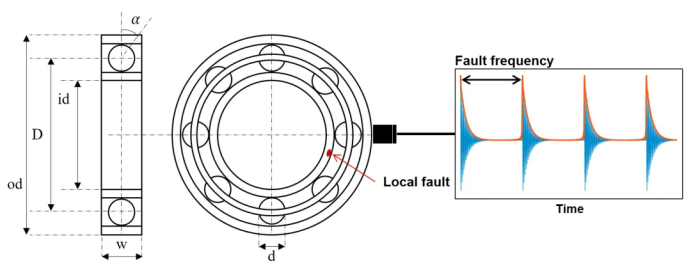
4. Application of vibration monitoring in rail transit
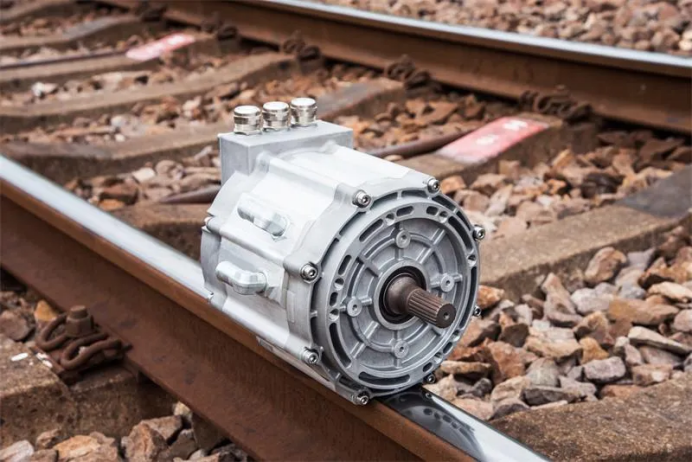
1. Drive the motor bearing
Application background drive motor bearing bears large radial and axial load under high speed rotation, and vibration monitoring can capture the deterioration signal of bearing in real time.
Monitoring focuses on mutations in high-frequency vibrational signals, especially in the contact regions of the inner circle and the rolling body.

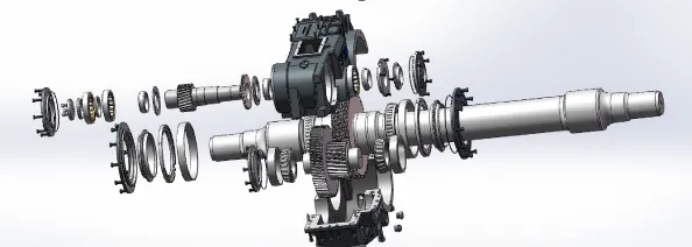
2. Gearbox bearing
The applied background gearbox bearing bears the complex load, and the vibration signal is susceptible to the gear engagement noise interference.
The monitoring focuses on separating the bearing fault signal through the envelope demodulation technology, and pays attention to the roller path spalling and the abnormal holder.
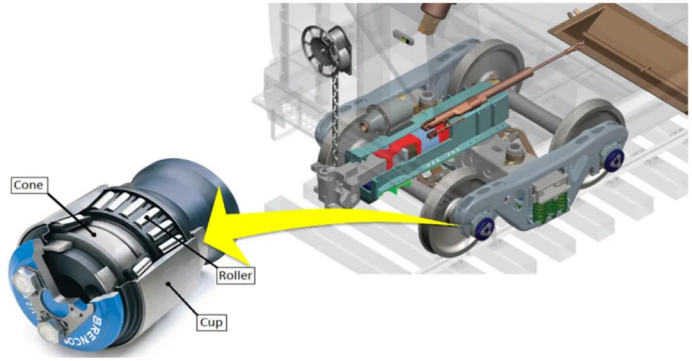
3. Shaft box bearing
Application background The axle box bearing directly carries the weight of the train, and its failure may lead to major safety risks.
Monitoring focus on regular monitoring of low frequency vibration signal, pay attention to the lubrication state and roller surface defects.
5. How to optimize the vibration monitoring system
1. Sensor arrangement
In the key parts, the acceleration sensors are installed on the bearing housing to improve the accuracy of signal acquisition.
Select a wide band, high sensitivity sensor to ensure capturing tiny vibrations.
2. Real-time data analysis
Use an online monitoring system to process the vibration data in real time.
Equipped with automatic alarm function, when the vibration exceeds the preset threshold.
3. Maintenance strategy optimization
Implement a state-based maintenance strategy (CBM) combined with vibration monitoring data.
Calibrate the vibration monitoring equipment regularly to ensure the data reliability.
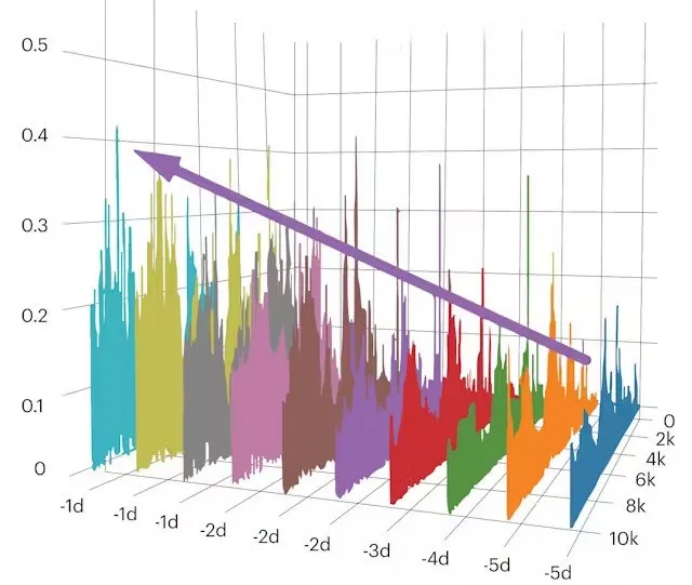
Vibration monitoring is an important means of bearing fault prediction. By analyzing the vibration signal, the bearing potential problems can be identified in the early stage to avoid the serious impact of fault expansion on the equipment. In the field of rail transit, the vibration monitoring of drive motor bearings, gearbox bearings and axle box bearings is very important, which can not only improve the safety and stability of equipment operation, but also greatly reduce the maintenance cost. With the continuous progress of vibration monitoring technology and data analysis methods, the accuracy and efficiency of bearing fault prediction will be further improved, providing a more reliable guarantee for the efficient operation of the equipment.