Hot Keywords:
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 4 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-04 Origin: Site
The discontinuity of metal materials refers to the non-uniformity and abrupt changes in their internal structure, composition, or properties. In failure analysis cases, it is found that many failures are caused by the discontinuity of materials. The discontinuity of structures is mainly reflected in two aspects: internal defects and the non-uniformity of the organization:
Internal defects:
Porosity. During the metal melting and casting processes, gases that fail to escape in time form cavities within the metal. These porosities disrupt the metal's continuity, reducing its effective load-bearing area and leading to a decrease in strength and toughness. Welded joints often contain varying degrees and quantities of porosity.
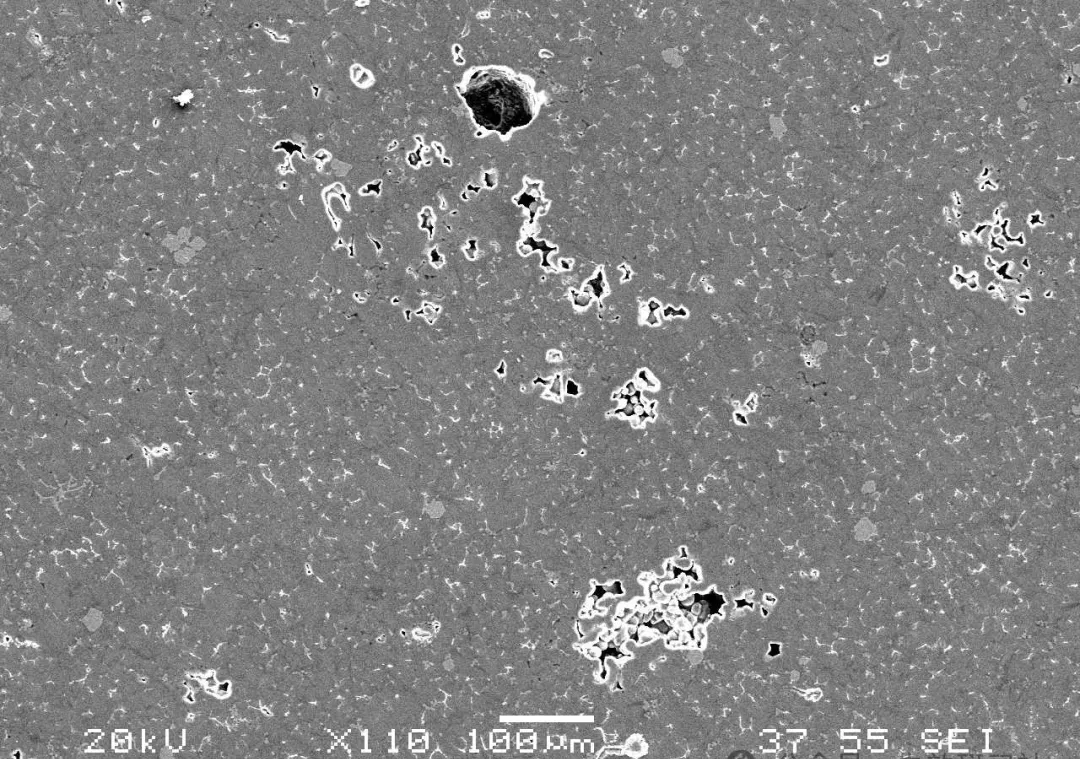
Shrinkage and shrinkage: the holes formed in the casting due to the volume contraction of metal during the solidification process. Usually concentrated in the last solidified part of the casting, it will make the metal structure discontinuous and reduce the mechanical properties and processing properties of the casting.
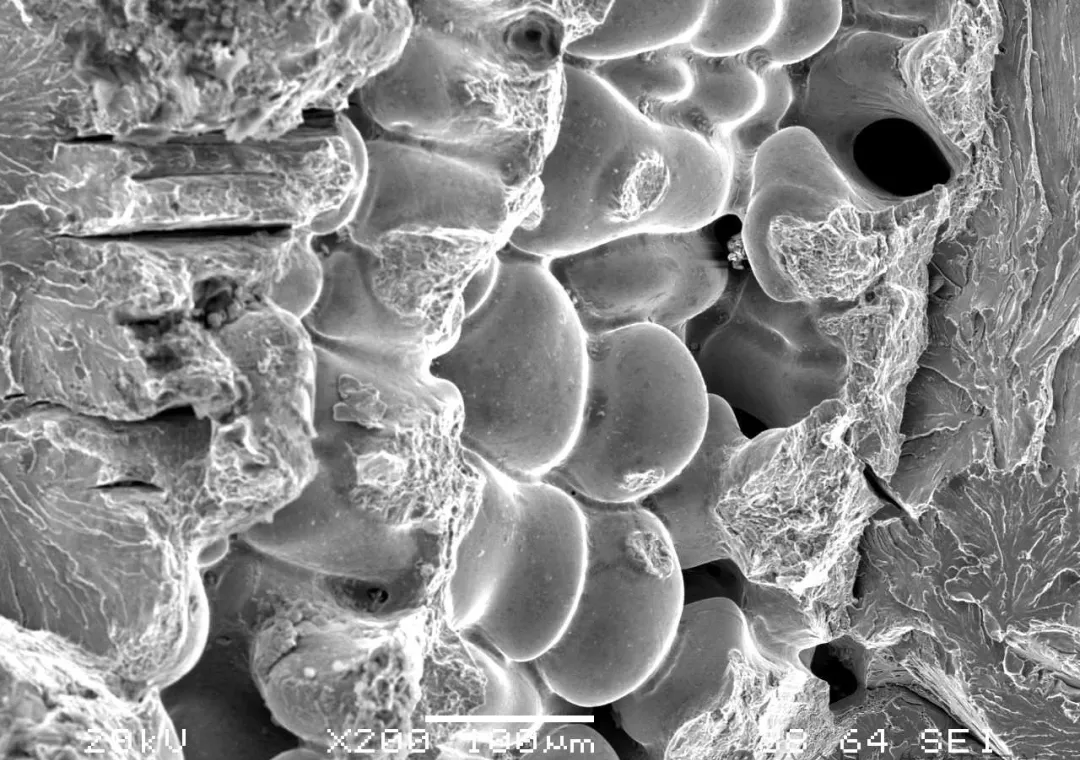
Cracks: Cracks are cracks that form in metals during processing or use due to stress concentration, fatigue, brittleness, and other factors. These cracks are serious discontinuity defects that can act as stress concentration sources, causing metal materials to fracture under stresses far below their ultimate strength limits, significantly reducing the material's reliability and service life.
Inhomogeneous organization and grain size: metal materials are composed of many grains. If the size of grains varies greatly, the deformation degree of different sizes of grains is different under force, and stress concentration is easy to occur at grain boundaries, resulting in discontinuity of mechanical properties of materials.

• Inhomogeneous phase composition: Metal materials may contain multiple phases, such as ferrite, cementite, and pearlite in iron-carbon alloys. These phases have different properties, and the atomic arrangement at their interfaces is discontinuous. When the material is subjected to force or heat, these interfaces can become weak points, affecting the overall performance of the material. • Second-phase particles or phases: Foreign matter second phases mainly originate from the solidification process of metal smelting. For example, elongated sulfide inclusions can fragment the matrix structure, significantly reducing the material's lateral properties.
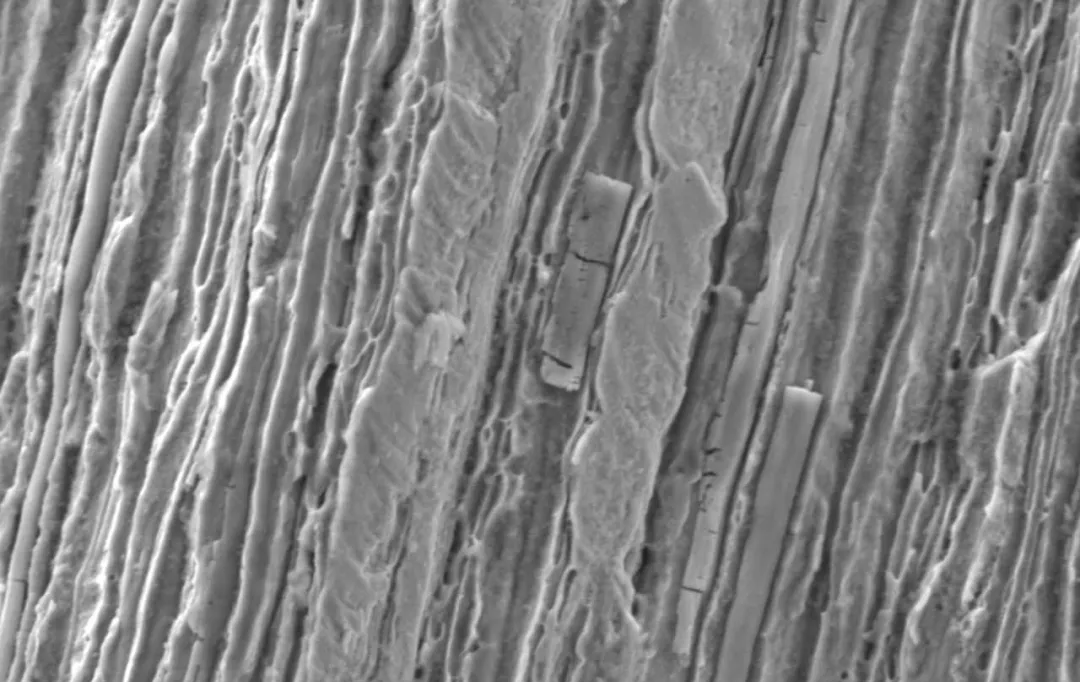
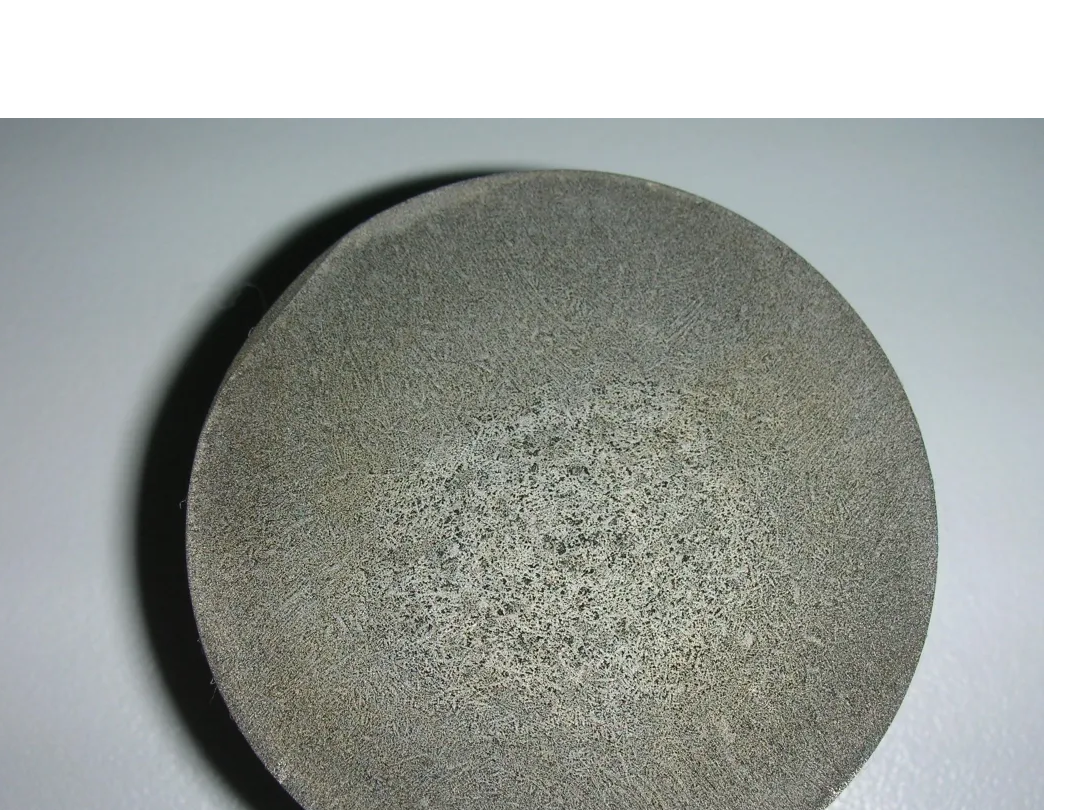
The discontinuity of components is primarily due to segregation: during the solidification of metals, uneven cooling rates and other factors can cause alloy elements to be distributed unevenly over a wide area. For example, in large ingots, there may be significant differences in chemical composition between the bottom and top, which can lead to variations in material properties across different sections, posing challenges for subsequent processing and use.

Not only do discontinuities in composition and microstructure occur during the smelting and casting of metals, but they also arise during subsequent cold and hot working and heat treatment processes: • Cold work hardening: During cold working, metal grains deform, increasing dislocation density, which results in higher strength and hardness while reducing ductility and toughness. This performance change is discontinuous between the processed and unprocessed areas, affecting subsequent processing and use. • Uneven heat treatment: If metal materials are heated or cooled unevenly during heat treatment, it can lead to inconsistent microstructural transformations in different parts of the material, resulting in performance variations. For example, during quenching, the cooling rate of the surface and core of a part can differ, leading to a high surface hardness and low core hardness, creating a discontinuity in performance.